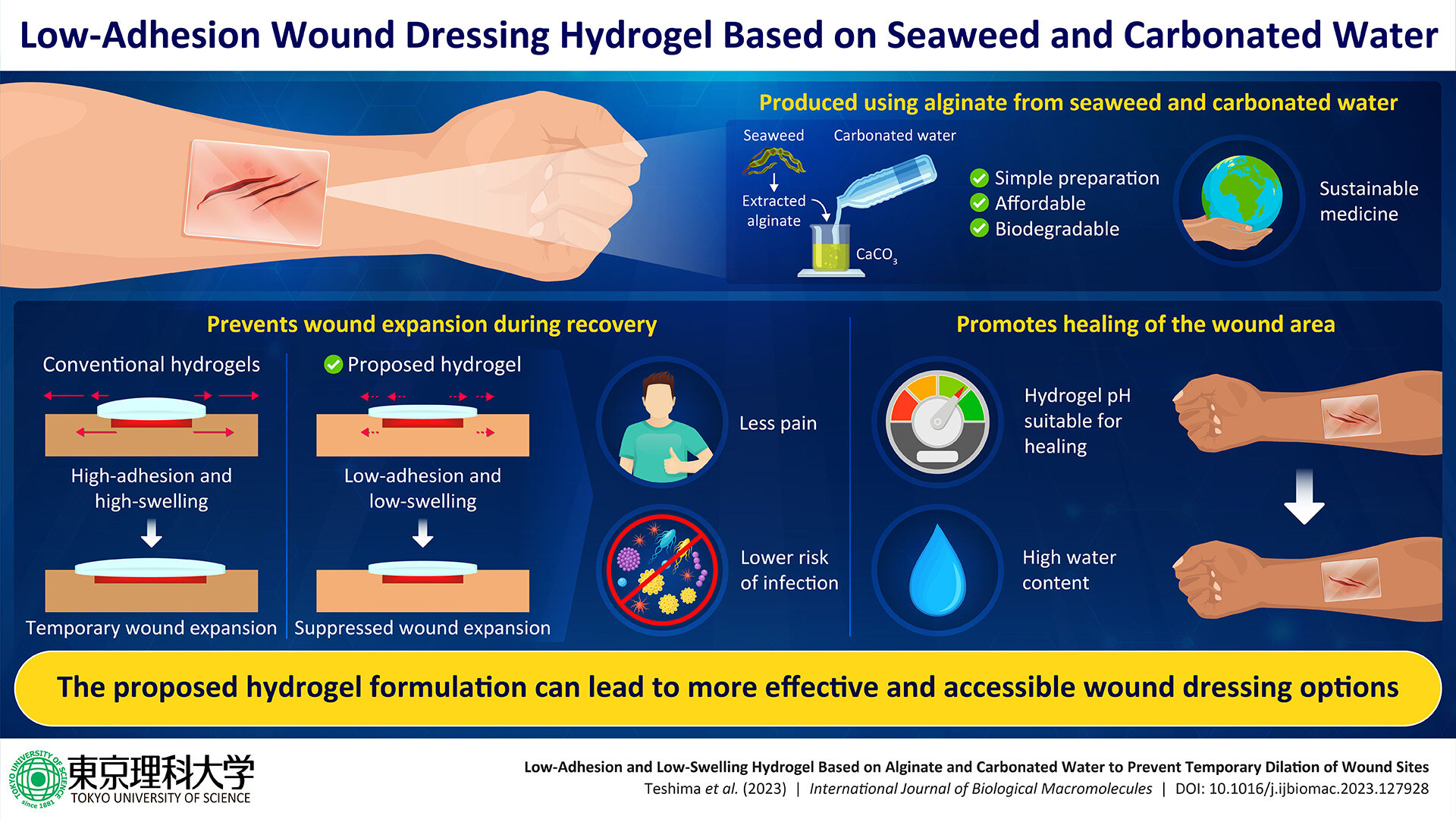
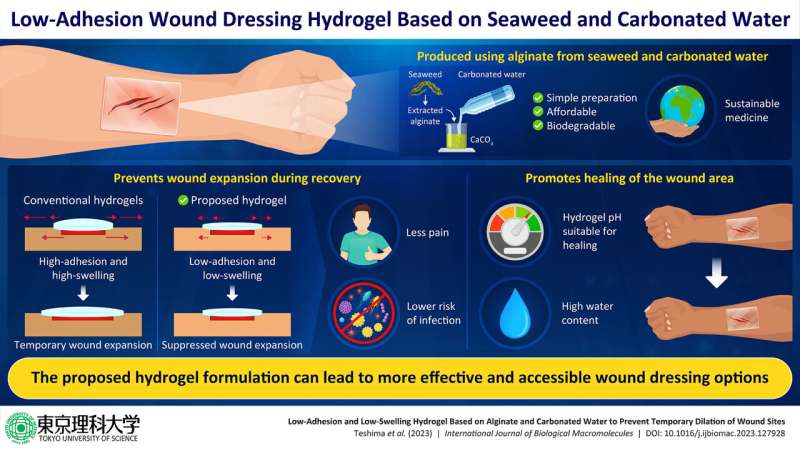
Alginate is a biocompatible and biodegradable substance found in seaweed. Now researchers from Tokyo University of Science have used alginate from seaweed washed ashore, CaCO3, and carbonated water to develop a hydrogel that exhibits lower skin adhesion and swelling. These properties, although the exact opposite of conventional wound dressings, can help prevent the expansion of the wound site during recovery and the obtained hydrogel has a high wound healing efficiency. Credit: Ryota Teshima of Tokyo University of Science
The skin is the largest and most important organ of the human body, acting as the main interface between the internal and the external world. It is frequently exposed to many types of physical injuries or wounds, including cuts, scrapes, scratches, infections, and ulcers.
Unfortunately, as one ages, the skin becomes weaker and less able to heal itself without help. With many countries experiencing a rapid increase in the aging population, the demand for the treatment of such skin wounds has created a greater need for accessible and effective wound care products.
Over the past few decades, hydrogels have received much attention for the treatment of skin wounds. When applied over a wound, these special gels can promote healing by absorbing released fluids (exudates) and keeping the wound protected, well hydrated and oxygenated.
However, most developed hydrogels gain adhesive properties to skin tissue to follow skin movement. Since these hydrogels are tough and stick to the skin and wound site, they stretch and expand the wound itself once they swell after absorbing exudates.
This not only causes pain to the user, but also puts them at a higher risk of bacterial infection due to the wound area expansion. Therefore, to create hydrogels that can effectively treat wounds without interfering with the wound healing process, it is necessary to experiment with the preparation of hydrogels based on new ideas while existing material properties.
Against this background, a team of researchers from Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has now proposed an innovative and highly additive medical material for the treatment of skin wounds.
As reported in their recent study published in the International Journal of Biological Macromoleculeshave developed a new, low-cost hydrogel using a component found in seaweed, which achieves physical properties completely different from those of conventional hydrogel.
The study was led by Mr. Ryota Teshima, a master’s student at TUS. Assistant Professor Shigehito Osawa, Ms. Miki Yoshikawa, Associate Professor Yayoi Kawano, Professor Hidenori Otsuka, and Professor Takehisa Hanawa, all from different faculties and departments at TUS, were also part of this study.
The method of preparation of the proposed hydrogel is quite simple. It is made using alginate, calcium carbonate, and carbonated water. Alginate is a biocompatible substance that can be extracted from beach-cast seaweed.
Most importantly, it does not adhere strongly to cells or skin tissues. Thanks to the special structure formed by alginate and calcium ions, in addition to the protective effect of the CO2 in carbonated water against acidification, the resulting hydrogel not only exhibited ideal pH and moisture conditions for wound repair, but also showed significantly lower adhesion and swelling, compared to other commercial hydrogel wound dressings.
The researchers tested the effectiveness of their new hydrogel using cell cultures and a mouse model, both of which yielded excellent results.
“By animal experimentsdemonstrated that our hydrogel has a high therapeutic effect and at the same time can suppress the temporary expansion of the wound area caused by conventional clinical preparations,” says Mr. Teshima. “This proves our initial hypothesis that gels with low skin adhesion and low- swelling properties are excellent as a wound dressing material, which is the opposite of conventional wisdom.”
Notably alginate can be extracted from beach-stranded seaweed, a renewable resource often considered a coastal waste material. As the proposed hydrogel is not only cheap but also biodegradable, this development is an important step towards future advances in sustainable medicine.
“Medical materials still have a sustainability-oriented perspective, and we believe this research will serve as a benchmark for the design of future medical materials and lead to sustainable and low-cost wound care,” says Mr Teshima. “Furthermore, our findings can help clarify issues hydrogel formulations currently in clinical use and provide new design guidelines for the next generation of wound treatment gels.”
More information:
Ryota Teshima et al, Low-adhesion and low-swelling hydrogel based on alginate and carbonated water to prevent temporary dilatation of wound sites, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127928
Provided by
Tokyo University of Science
Quotation: Researchers develop sustainable wound dressing hydrogel based on seaweed and carbonated water (2023, December 15) retrieved December 16, 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-12-sustainable-wound-hydrogel-based-seaweed.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any fair transaction for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/how-to-free-rubies-family-island-game-2023-youtube-1001724707
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/hay-day-hack-mystery-box-and-diamonds-2022-cheater-1001724823
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/litmatch-unlimited-diamond-premium-free-apk-2023-l-1001724890
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/myths-of-moonrise-kody-na-stycze-2023-gamegift-nYd-1001724947
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/pull-the-pin-hack-mod-unlocked-no-ads-153-0-1-modp-1001725100
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/evony-mod-apk-v4-39-0-unlimited-everything-apkmodg-1001725171
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/dice-dreams-rewards-app-free-rolls-and-dice-app-ap-1001725267
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/project-makeover-unlimited-coins-mod-apk-free-down-1001725395
https://www.deviantart.com/
https://www.deviantart.com/pihow19094/journal/How-to-Get-TikTok-Coins-Effortlessly-rFth-1001725543
TikTok Coin Hacks: The Complete Guide
TikTok Coin Hacks: Boost Your Account for Free
Free TikTok Coins: The Real Deal
TikTok Coin Hacks: The Complete Guide
Come Ottenere Monete TikTok Gratis: Strategie Comprovate
Free TikTok Coins: The Holy Grail of Success
Découvrez le pouvoir des pièces gratuites sur TikTok
Are TikTok Coin Generators Worth It?
Aprovechando al Máximo los Regalos de Monedas TikTok
TikTok Coin Generator Scams: Avoiding Pitfalls
TikTok Coin Generator Risks: The Truth
Boost Your TikTok Engagement with Free Coins
Le hack des pièces gratuites sur TikTok pour les passionnés du jeu




